-
Prospective Evolution of Li-ion Battery Cathodes
Posted on 2023-01-23
-
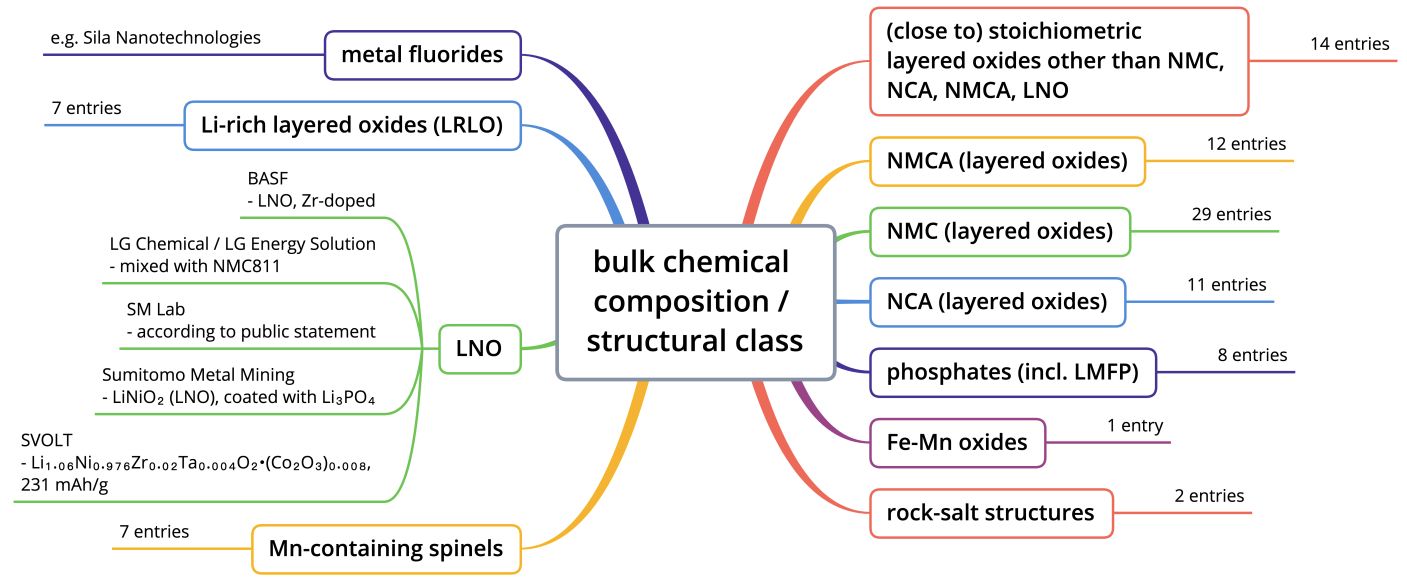
Ni / Mn-containing cathode active materials (such as NMC, NMCA, Co-free NMx) typically account for >50% of overall Li-ion battery cell materials costs.
-
For this reason, Li-ion battery cell manufacturers are continuously evaluating if a replacement with lower cost cathode materials is feasible:
-
by relying on lower-cost raw materials, such as Fe & Mn,
-
or through reduced manufacturing process costs (such as metal-to-cathode).
-
Recent developments (within the frame of liquid electrolyte Li-ion battery cells) suggest that two positive electrode material technology tracks will split up most electrified transport applications between them:
-
cells with Ni-dominant positive electrode active materials, 90 to >99 mass% Ni (in relation to the total transition metal content), theoretical limit for LNO (LiNiO2): 275 mAh/g reversible capacity, 3.8 V vs. Li+/Li average potential.
-
cells with iron-based LFP (LiFePO4) positive electrode active materials, theoretical limit: 170 mAh/g, 3.43 V vs. Li+/Li average potential. These materials will evolve towards iron / manganese-based LMFP with increasing Mn content, theoretical limit for LMP (LiMnPO4 170 mAh/g, 4.1 V vs. Li+/Li.
-
Sign up for free on b-science.net or request a quote for a premium subscription.
-
This post was also published on LinkedIn.
|